The shaft is an important component of the motor. The shaft is pressed with an iron core and a commutator. The iron core is embedded with windings, and then bearings and other components are pressed to form an armature component. The material, structure, and process quality of the shaft have a direct impact on the performance of the motor.
1. Structural type of shaft
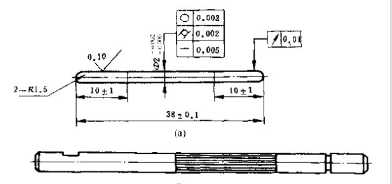
There are many types of shafts for micro motors, which can be classified according to different methods. (1) According to the classification of structural type and manufacturing process, the optical axis has a full optical axis, as shown in (a) in the figure. The basic dimensions and tolerances of its outer diameter are the same along the entire length. The iron core section or commutator section of the optical axis can be in the form of knurling and reinforcement. At this point, the outer diameter of the shaft is basically the same, but the diameter of the knurled or ribbed section needs to expand. About 0.01-0.05 millimeters for pressing into the iron core or commutator. The reinforcing bar structure can be stamped with specialized upper and lower molds, and the shaft will not bend or deform, resulting in high production efficiency. The axial extension section of the optical axis can have various types of axial extension specified by standards, and non-standard axial extensions can also be used if necessary.
② Step shaft, as shown in Figure 7-3, is a cup shaped rotor shaft of an AC servo motor. The material is 45 steel, with a margin of 0.2mm left in the two bearing sections. After holding the metal cup, it is precision machined. Step shaft is a major structural form of the shaft in micro motors. The step axis consists of steps at one end, steps at both ends, and steps formed by an optical axis pressure ring. Considering material utilization and processing time, the number of steps should be minimized as much as possible.
Motor shaft structure diagram
(2) Classified according to different materials, 1. Magnetic material shaft: Some micro motors require the shaft to have magnetic conductivity because the iron core section of the shaft is part of the magnetic circuit. High quality carbon steel (20~45 grade medium carbon steel) can be used, and alloy structural steel (such as 5OMn, 40Cr, etc.) can be used for special purposes. Some shafts with less force can be made of ordinary carbon steel.
2 Non magnetic material axis
Some micro motors require the shaft to be non magnetic in terms of magnetic circuit structure, such as when there are permanent magnets with axial or tangential magnetic circuits on the rotor (permanent magnet induction motor, permanent magnet synchronous generator, etc.).

